Tidy Data
Lecture 8
Duke University
STA 199 - Summer 2023
2023-09-21
Checklist
– Clone ae-07
– Make sure you are keeping up with Preparation Videos / Readings
– Make sure you are keeping up with Slack
– HW-1 grades are released
— Look through feedback (after class)
— Please visit office hours if you have content questions
— Please review regrade submission guidelines on Syllabus
– Exam I released September 28th ~ 5:00 PM
Announcement
– Do not amend commits
Amending a commit is a way to modify the most recent commit you have made in your current branch. This can be helpful if you need to edit the commit message or if you forgot to include changes in the commit.
But why? Just make another commit….
Merge Conflict: You changed an existing pushed commit, creating your own version.
Warm Up: Joins
Warm Up: Joins
inner_join(x2, y2, by = c("value"))
inner_join(x2, y2 , by = c("value" , "value2"))
Warm Up: Joins
Warm Up: Joins
Joins Summary
– There are many ways to join data
– Let the join criteria choose the function for you
– Data sets are joined by a “key”
– The key(s) default to common names across data sets unless specified
– Can join on variables with different names by using the = sign
by = c("variable1" = "variable2")
Forms of Data
Data Format (Wide vs Long)
– Wide data contains values that do not repeat in the first column
– Long data contains values that do repeat in the first column
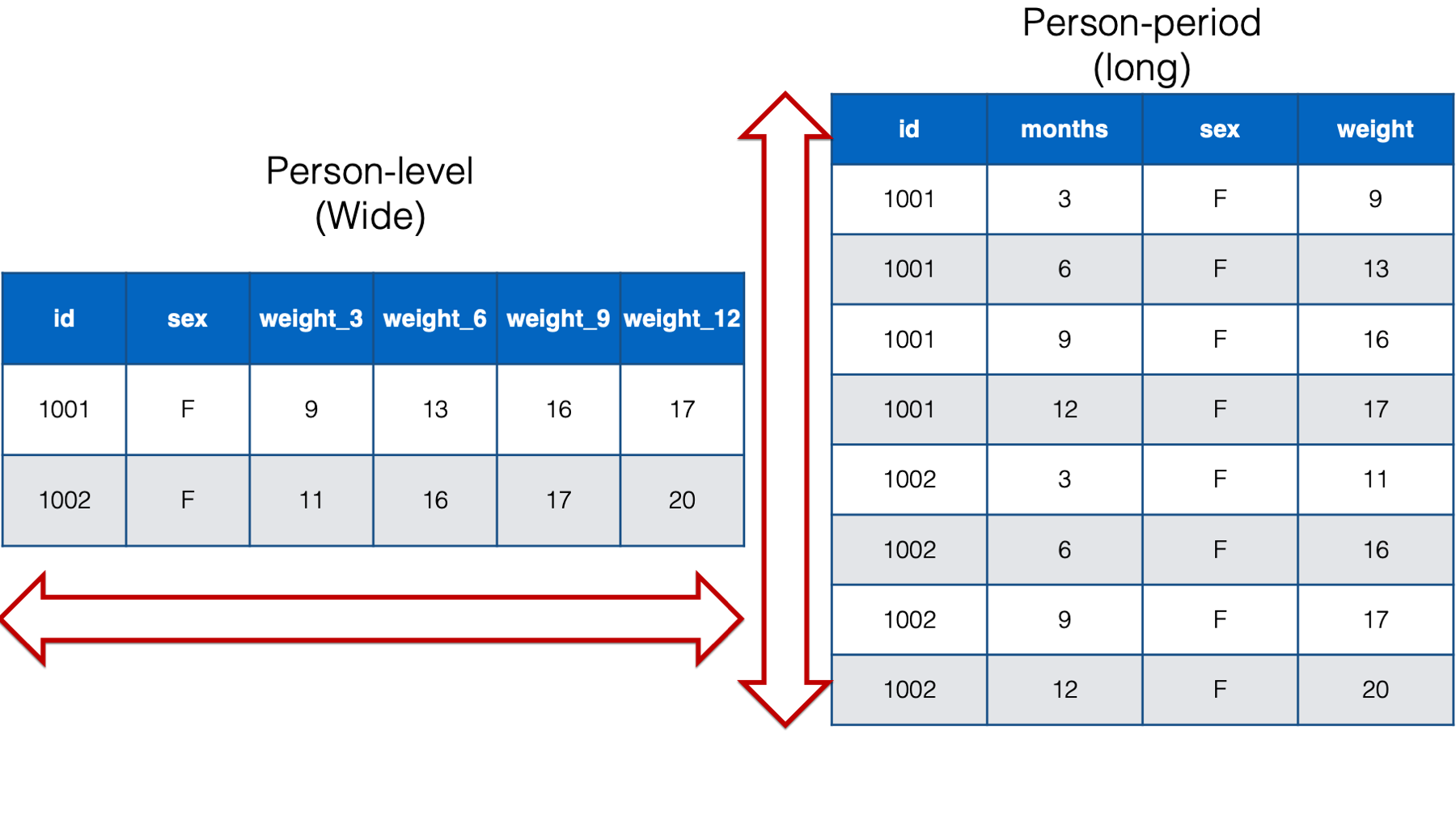
Data Format (Wide vs Long)
– Which have we typically used to create plots in this class?

Tidy Data
There are three interrelated rules that make a dataset tidy:
Each variable is a column; each column is a variable.
Each observation is row; each row is an observation.
Each value is a cell; each cell is a single value.
Motivation
– Sometimes, data are not in this format…
pivots
– pivot_longer
– pivot_wider
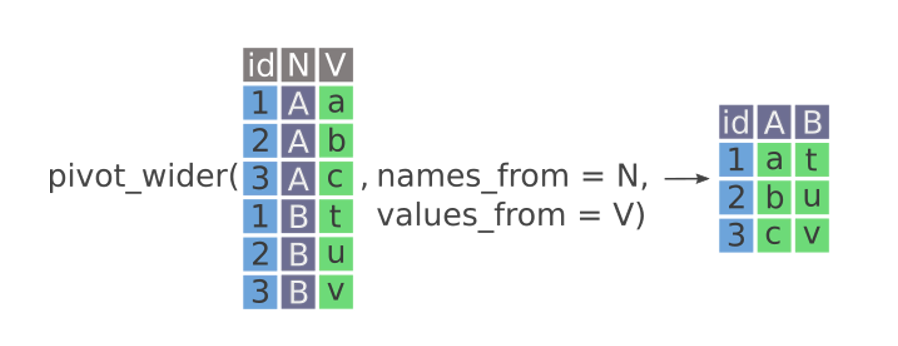
pivot_wider
pivot_wider
– Making tables for quick comparison / display purposes
– names_from
– values_from
ae-07
R-practice: Recreate